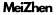Industrial Woven Mesh Technical Support
Knowledge Point Introduction:
1:Basics of Wire Mesh
2:Wire Used to Make Wire Mesh
3:Uses for Wire Mesh
Basics of Wire Mesh
Wire mesh is fabricated by the intertwining,weaving,or welding of wires of various thicknesses to create proportionally equal parallel rows and intersecting columns.Also known aswire fabric,wire cloth,or hardware mesh,the production of wire mesh involves the weaving of wire on industrial looms,leaving square or rectangular gaps between the wires.Weldedwire mesh or fabric is manufactured using an electric welder that joins parallel longitudinal wires where the wires intersect.
There are a limitless number of shapes,sizes,and configurations of wire mesh made from an assortment of highly durable and resilient materials whose major function is to separate,screen,structure,and shield various applications and processes.The types of wire include galvanized steel,stainless steel,aluminum,steel,and copper alloy wire.The type ofapplication,necessary tensile strength,durability,longevity,and required flexibility are some of the factors used to determine the desired type and style of wire.
How Wire Mesh is Made
The processes used to produce wire mesh are weaving and welding,with wire weaving being similar to the weaving of cloth on a loom,while welding is used to join the wires where they intersect.Both processes are completed using pre-programmed machines.
Wire Weaving
Near the end of the 17th century,woven wire cloth for the mining and pulp industries came into high demand,leading to the development of wire weaving looms.Over the centuries,the use for wire mesh has advanced beyond mines and pulp mills to architecture,plastic extrusion,aggregate screening,and filtration processing.The rise in demand has led to themodern industrial wire weaving industry.
- Weaving Loom —Weaving looms weave mesh rolls with widths of 48″,60”,72”,98″,or wider.The loom has a warp beam,heddle frames,a reed,a rapier for transporting weft wire,and a take-up mechanism.Manufacturers use looms to weave meshes of standard and custom patterns.The completed mesh rolls are cut to varying lengths depending on the needs of customer specifications.Wires woven horizontally or lengthwise are warp wires,while wires woven vertically or crosswise are referred to as weft wires or shute wires,terms commonly used in textilemanufacturing.
- Warp Beam —The warp beam is a cylindrical drum wrapped with the warp wires.The warp beam’s tension must be meticulously controlled to avoid elongation of the wovenmesh.The number of warp wires varies depending on the mesh width and must be kept the same length.
- Heddle Frames —The heddle frames separate the wires that are fed by the warp beam.Most looms have two heddle frames,with one used to lift half of the warp wires while theother pulls the warp wires down.The heddle frames change position as the weft wires move across the warp wires.
- Rapier Band —The weft wires are carried across the full width of the cloth by the rapier at each cycle of the heddle frame.It feeds a single weft wire between the sets of warpwires.
- Reed —The reed keeps the warp wires from the warp beam in place and accurately spaced and separated.Once the weft wire moves across the warp wires,the reed beats theweft wires tightly in place in the wire cloth.
- Take-Up—The take-up mechanism is a set of rollers that takes the fabric away from the loom with a pickup roller and two other rollers that work together to wind the cloth to thecloth roller.The fabric is wound in single layers with a smooth flat surface created by it being passed through the set of rollers.
Once the loom has been assembled and the warp beam loaded,the weaving process is completed automatically.As the loom begins,the warp beam unwinds in slow,evenincrements.In unison with the warp beam feeding the warp wire,the take-up mechanism winds the woven completed cloth in the same increments as the warp beam.Thesynchronized motion helps the loom maintain tension on the warp wires,which is a critical necessity for the production of high-quality cloth.

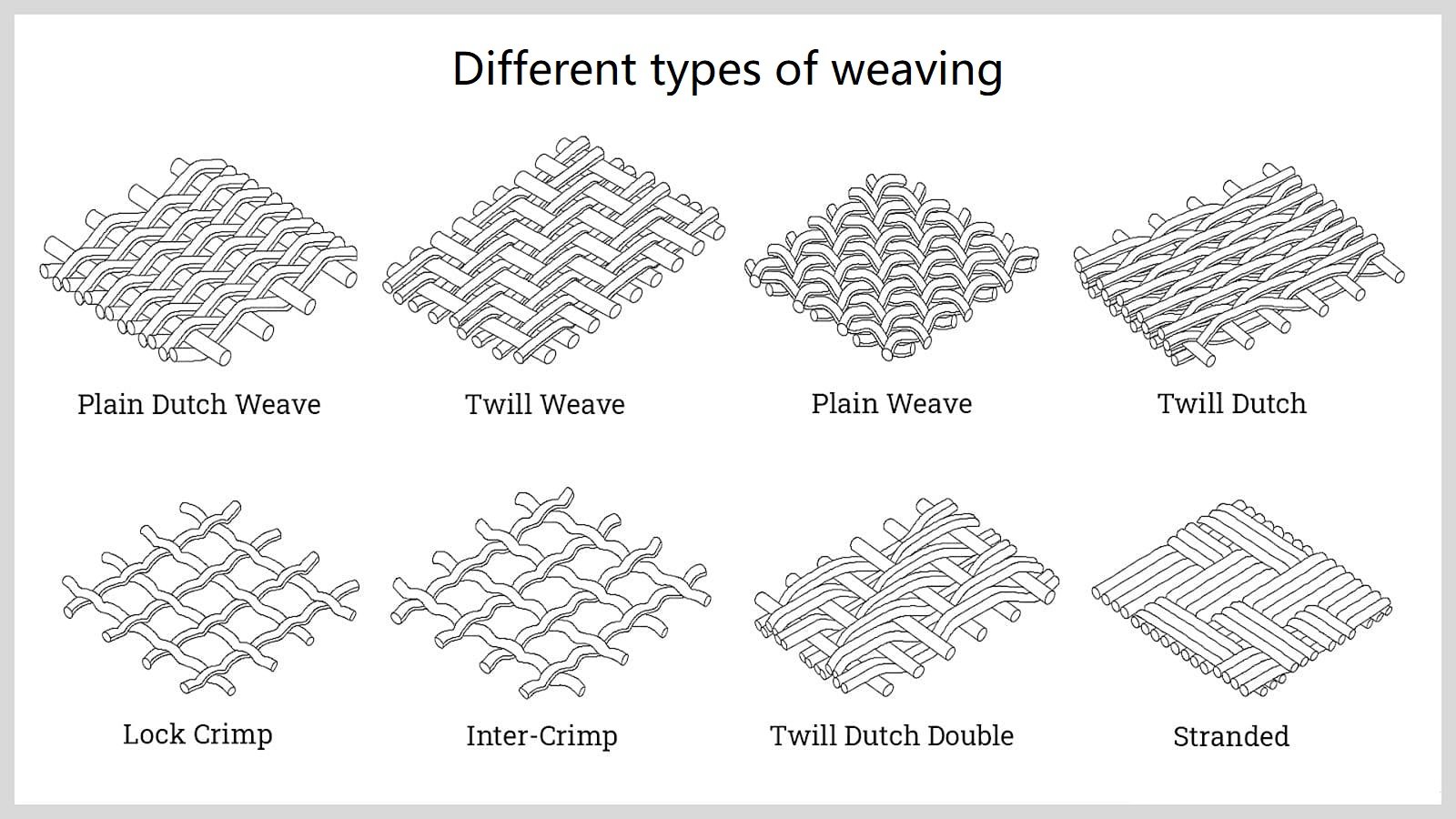
Stainless Steel Wire Mesh
Stainless steel wire mesh has all of the positive properties of stainless steel and provides high-quality protection and performance.Steel is widely used to produce wire mesh but rusts easily when exposed to the air.Stainless steel,which has the same compounds as steel,has chromium added that is rust-resistant and protects stainless steel from oxidation.
In wire mesh manufacturing,stainless steel is known for its reliability,sturdiness,and durability.The rust resistance of stainless steel makes it adaptable to any outdoor application.It consistently delivers strength and longevity,making it the most popular wire mesh form.
As with all forms of wire mesh,stainless steel can be welded or woven.The grades of stainless steel used to produce wire mesh are 304,304L,316,316L,321,347,or 430 in wirediameters ranging from 0.0085 inch (0.216 mm)up to 0.307 inch(7.8 mm).The openings of wire mesh change in accordance with the type of wire mesh.Openings that are less than 0.25 inch(6.35 mm)are classified as wire cloth.Critical factors for wire mesh are the percent of the open area and the weight of the mesh.
Grade 316 stainless steel is a premium alloy that is used for marine applications.It has exceptional corrosion resistance and is not affected by acids,salt water,or seawater,and comes in fine,medium,or coarse sizes.Stainless steel grade 304 is not as corrosion resistant as grade 316 but is exceptionally workable and less expensive than grade 316.
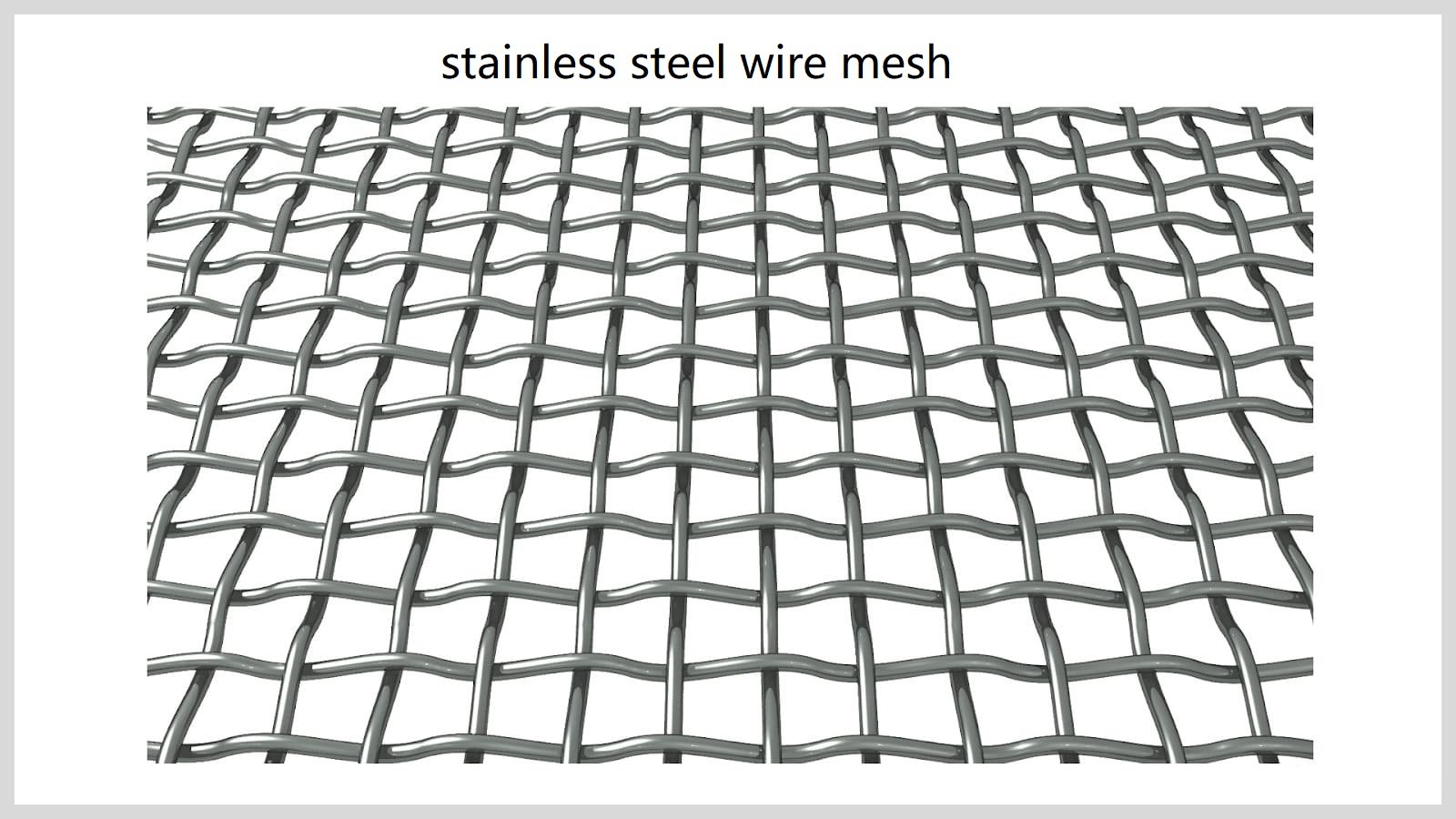
Wire Mesh Patterns
The pattern of wire mesh determines its capacity and how it can be used.There are an endless number of standard weave patterns and customized ones designed to fit a specificapplication.One distinction between the various paterns is whether the wire is crimped or not crimped,with crimping mechanically changing the contour of the weft or warp wires.
Crimped Wire Mesh
Crimped wire mesh is a square or rectangular weave that is woven using a crimping mesh machine.The processes used to produce crimped wire mesh involve compressing the wiresuch that the weft wire wraps over the warp wire and the warp wire wraps over the weft wire.The crimping process produces a bending effect on the wires such that they wrap overeach other.
- Pre-Crimp—Pre-crimped weaves are crimped with small folds or ridges that are added before the wire is woven to increase the strength and rigidity of the wire mesh.The processprevents the weft and warp wires from moving and keeps them secure.
- Lock Crimp—Lock crimp is another pre-crimp process that uses the grooves from the crimping process to lock the weave together at the intersections of the weft and warp wires.As with pre-crimping,the final weave is sturdier and immovable.
- Inter-Crimp —With inter-crimp,the warp and weft wires are crimped with additional crimps added between the intersections.It is a process used with fine wire with largeopenings to ensure the weft and warp wires are accurately and properly locked to provide additional rigidity.
Non-Crimped Wire
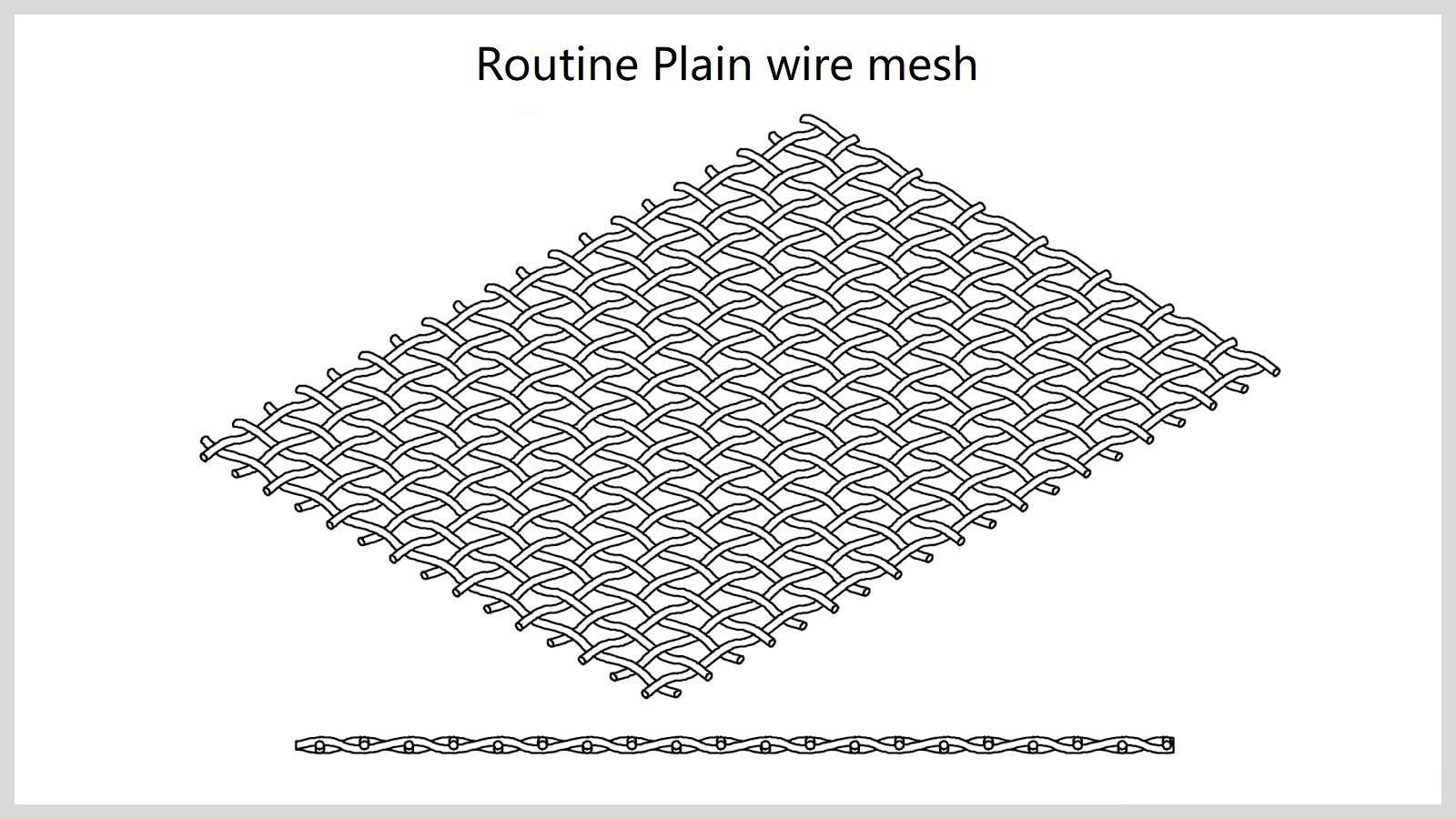
Non-crimped wire refers to plain wire mesh where the wire mesh is formed by a simple over-under weave of the warp and weft wires.The final product has a simple appearance with a smooth,even surface.Traditionally,non-crimped wire or plain wire has a higher mesh count.
Plain weave wire mesh is the most common of the wire mesh products.Wire mesh that has a 3 x 3 or finer wave has a plain weave pattern.It is commonly used for screening,such as screen doors and window screens.
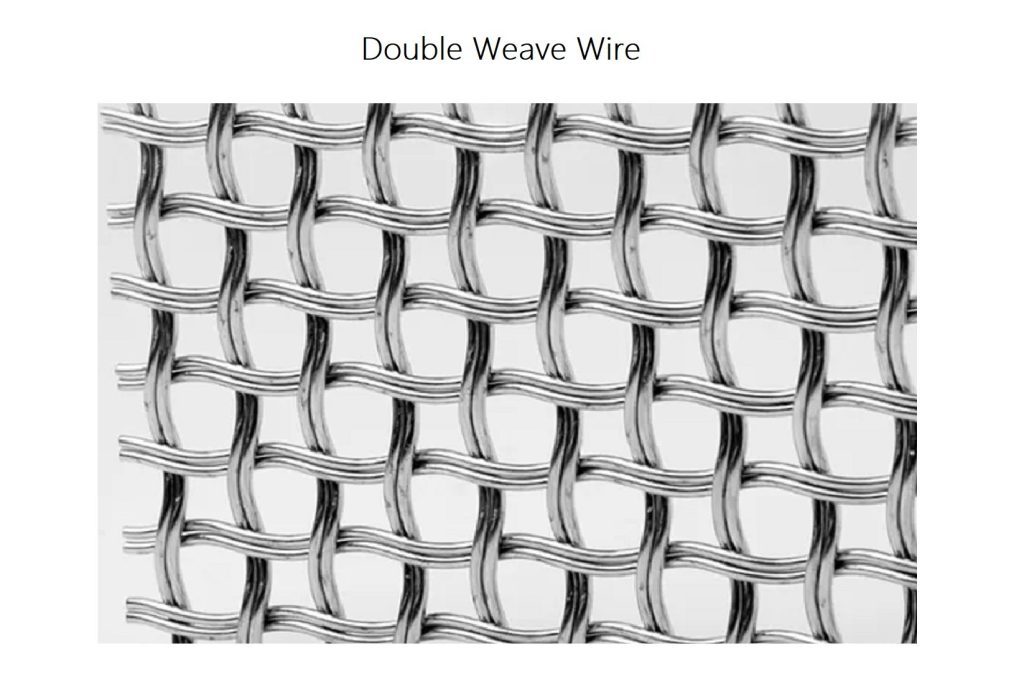
Double Weave Wire Mesh
Double weave wire mesh is a variation of the pre-crimped weave pattern.In the weaving process,the warp wires pass over and under two weft wires to form a wire mesh patterncapable of withstanding stressful and demanding uses.The double weave wire mesh pattern produces a wire mesh with extra durability for supporting vibrating screens in miningoperations and crushers,fences for farming,and screens for barbecue pits.
Flat Top Weave Wire Mesh
Flat top weave has non-crimped warp wires and crimped weft wires that create a sturdy,lockable wire mesh with a flat surface.It has a long abrasive life since no wires project fromthe top of the mesh to wear.Flat top weave wire mesh has little flow resistance,making it popular for architectural and structural applications requiring a smooth surface.A commonapplication for flat top weaves is for vibrating screens.

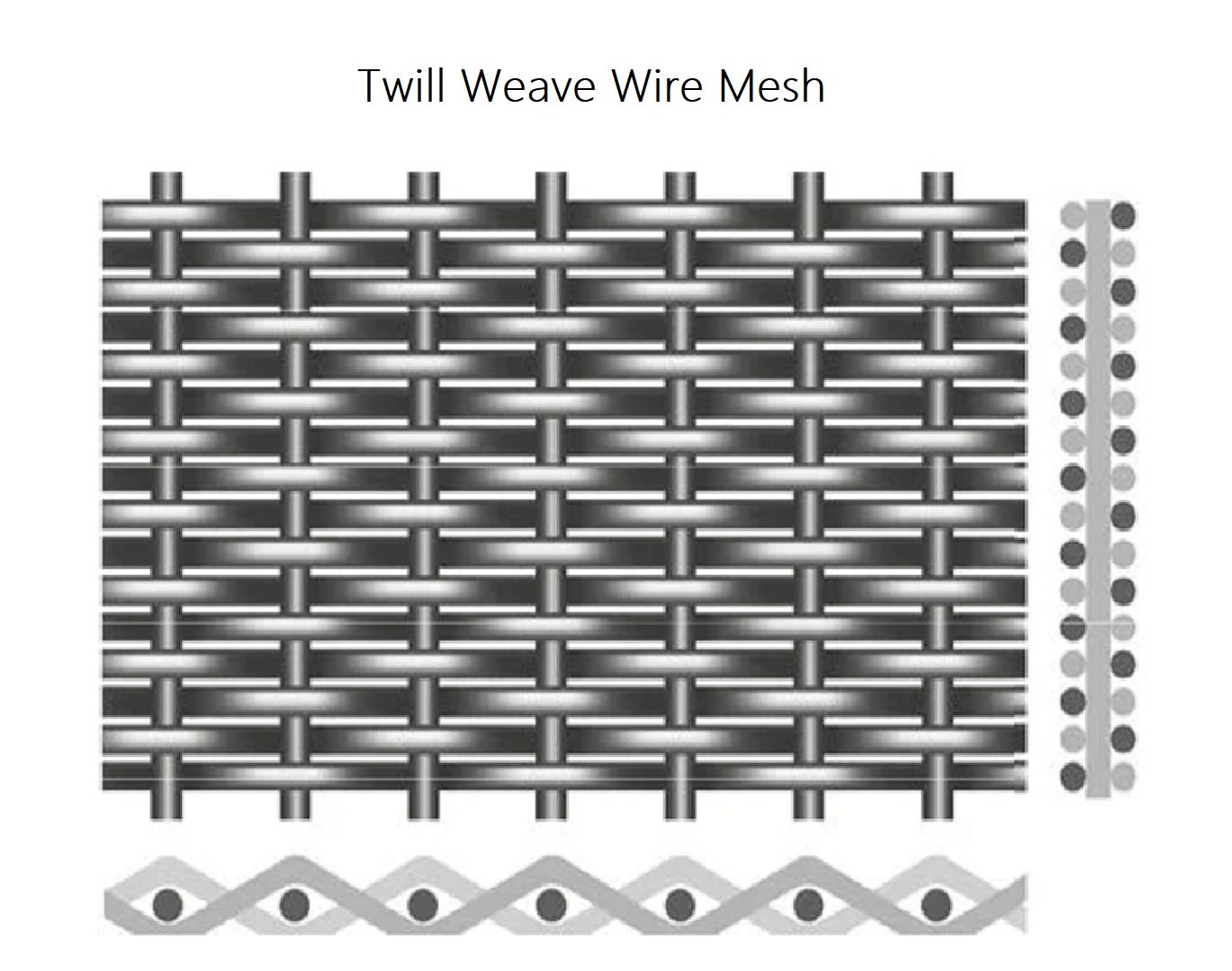
Twill Weave Wire Mesh
The twill weave pattern is ideal for weaving heavier and larger diameter wires.The pattern is formed by weaving warp wires over and under two weft wires or where a weft wire passesover and under two warp wires.The warp wire is inverted at the intersections to create a highly stable,rigid,and strong wire mesh.As the pattern develops,it becomes staggered,giving an appearance of parallel diagonal lines.
Twill weave wire mesh can support heavier loads and perform fine filtering.It is a basic component of the production of filters,colanders for aliments,chemical production,shielding,
and mosquito nets.For filtering processes,it is made of stainless steel grades 304 and 316 due to their resistance to acids and wear.
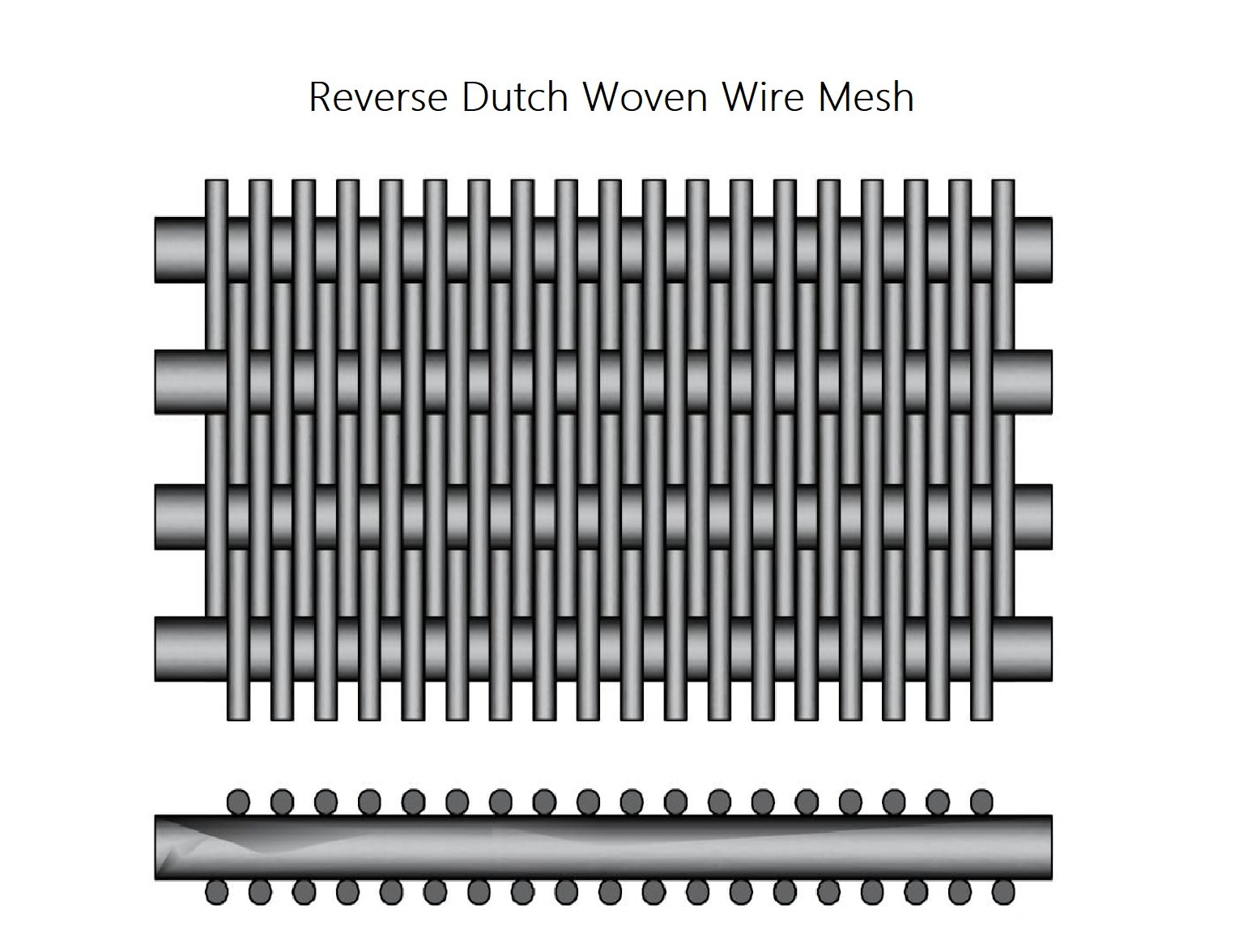
Reverse Dutch Woven Wire Mesh —Reverse dutch woven wire mesh is the same as plain dutch woven wire mesh.The difference between the two weaves is how the weft andwarp are woven,with the warp and weft wires being reversed.Thin warp wires are placed close together and woven with thicker weft wires,which creates higher strength in thewarp wires.The reverse dutch weave is used in applications that need wire mesh with acoustic properties,mechanical strength,and throughput filtration.
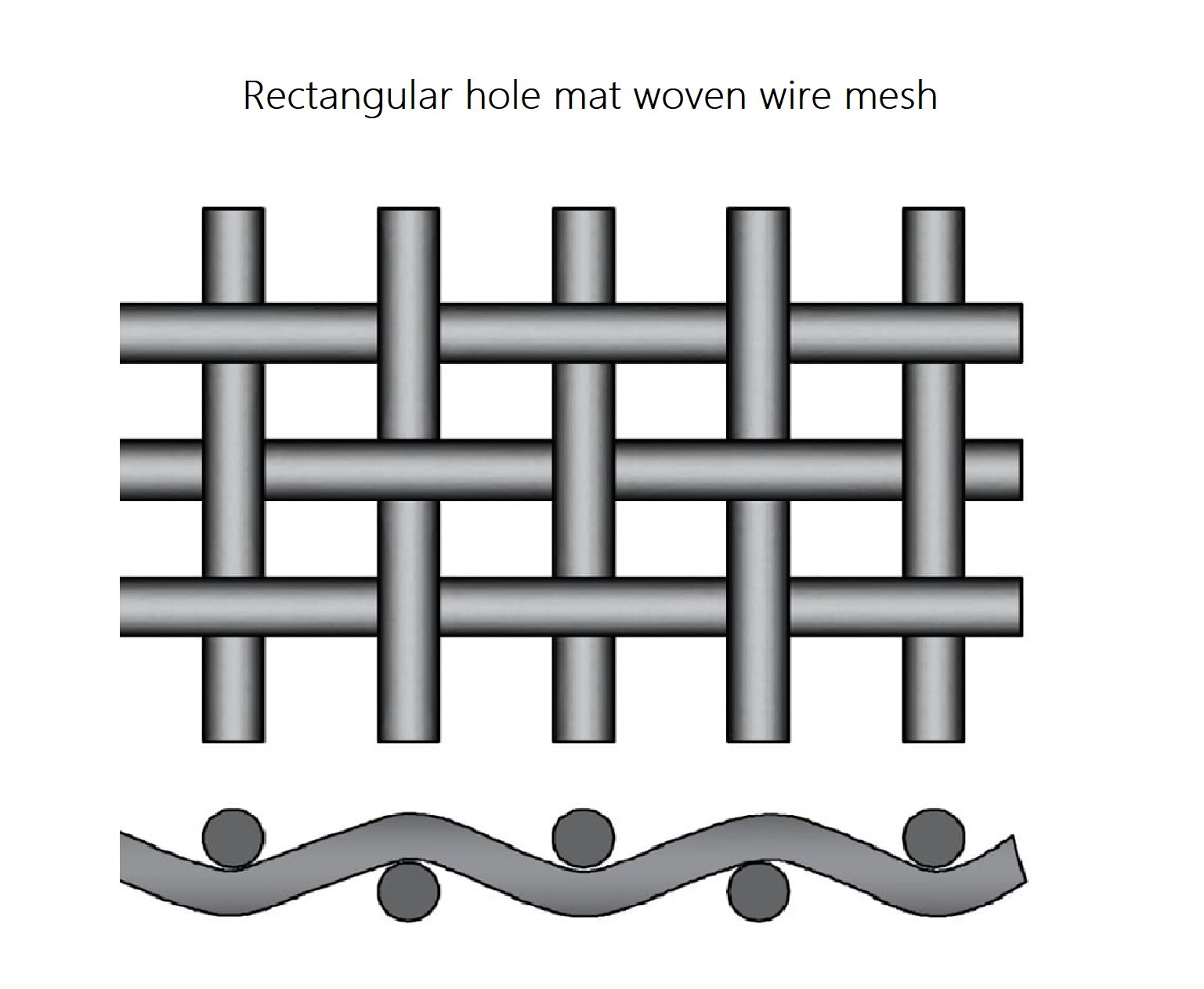
Rectangular Hole Mat Woven Wire Mesh
Rectangular hole mat woven wire mesh refers to wire mesh that does not have the same mesh count in both directions creating a rectangular rather than square mesh pattern.It is used in sifting and sizing operations to increase productivity and also where slight inaccuracies are not an issue.
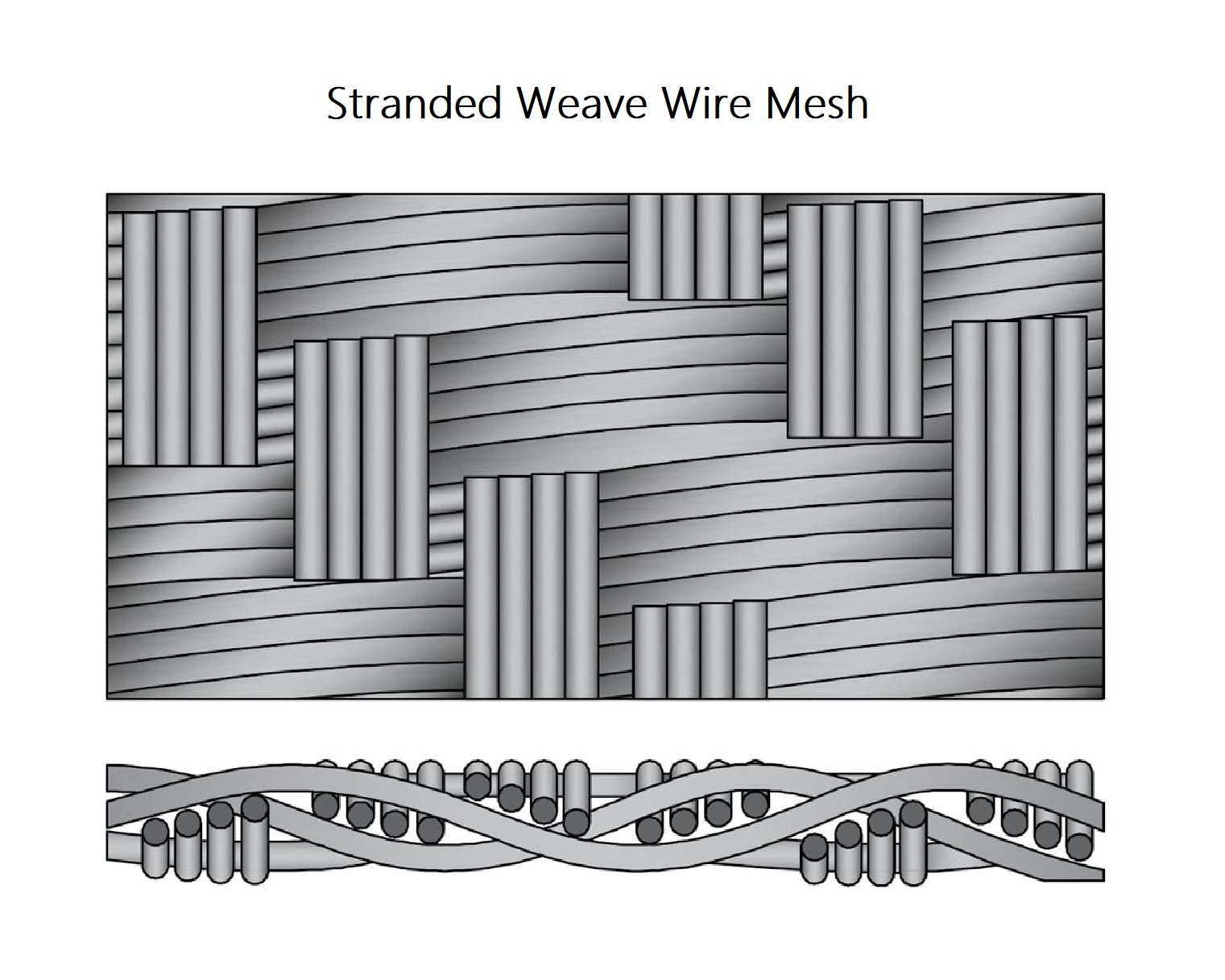
Stranded Weave Wire Mesh
Stranded weave wire mesh uses small-diameter weft and warp wire bunches that are woven in a plain square pattern.The use of multiple wires creates a twill style pattern that is extremely tight and strong.The tightness and density of the weave are useful in microfiltration cloth.
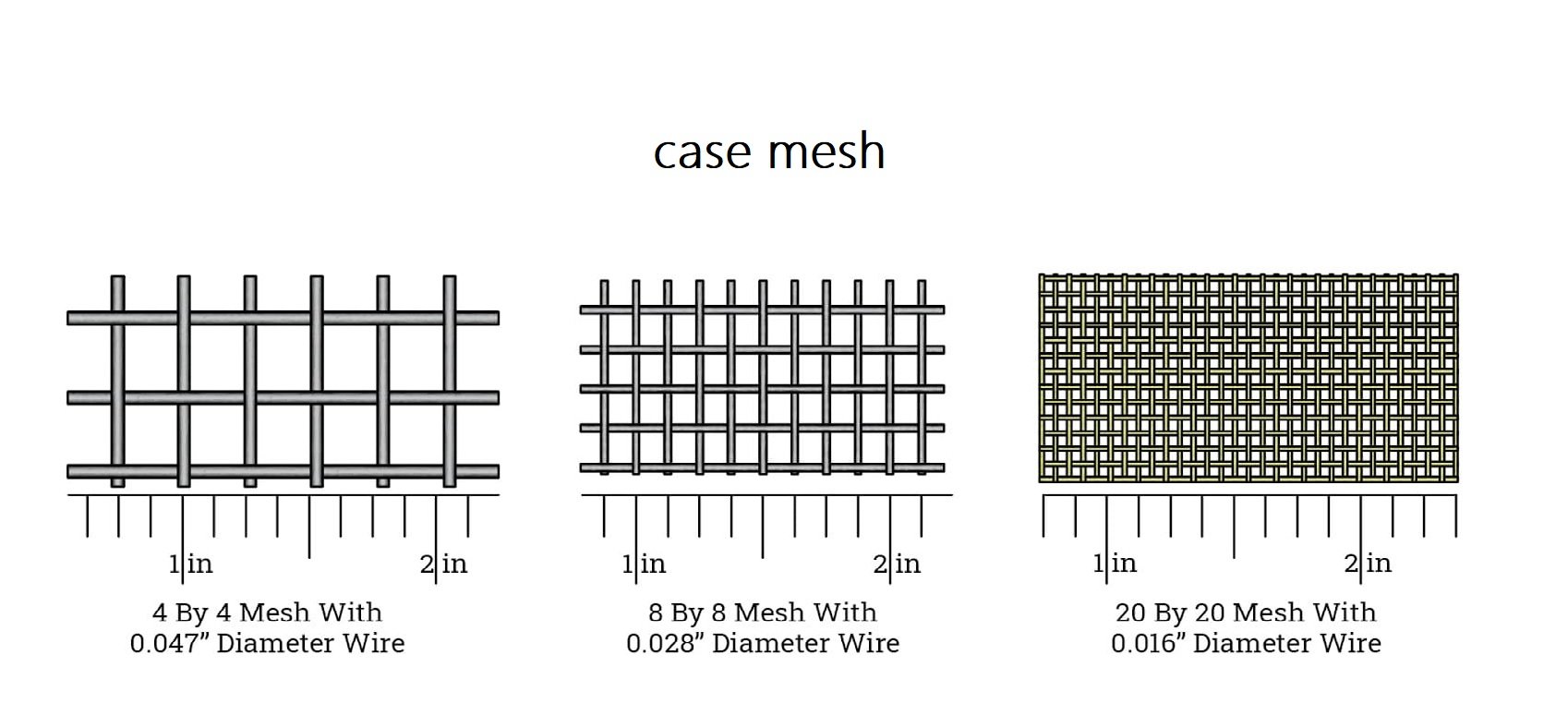
Mesh Count
The term mesh count refers to one of the most important principles of the wire mesh manufacturing industry.It is in regard to the number of openings per linear inch in wire mesh.The mesh count is determined by counting the number of openings in one linear inch from the center wire of a wire mesh.It is expressed as a single digit,such as .4 for a 4 by 4mesh or .20 for a 20 by 20 mesh.The number is an indication of the number of openings in one linear inch.
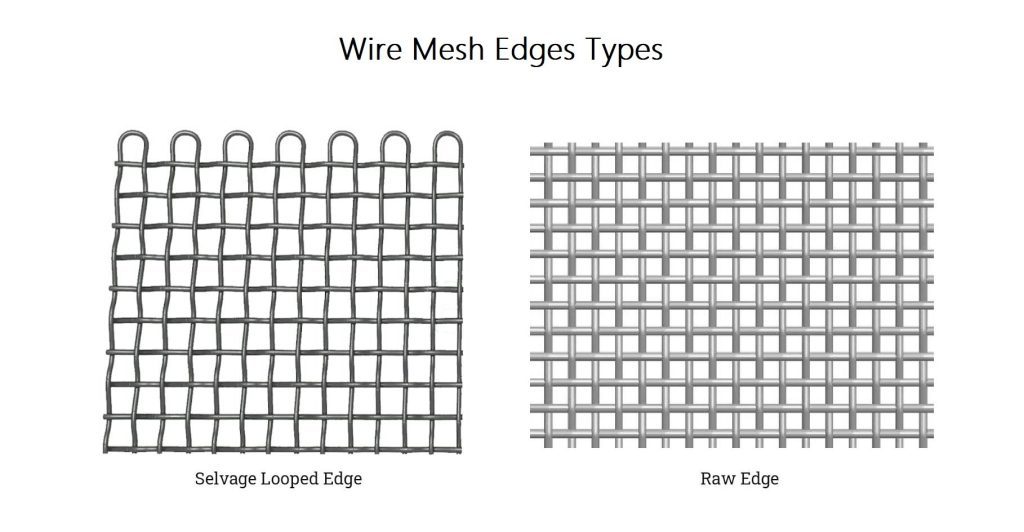
Wire Mesh Edges
The two forms of wire mesh edges are raw and selvage.When wire mesh cloth is woven,the weft wires form an edge along the length of the roll and prevent the mesh from unraveling.In the case of a raw edge,those weft wires are uncovered at the edge of the wire mesh.
With selvage edge wire mesh,the border of the wire mesh is finished to increase the stability of the mesh and protect workers when handling the mesh.There are various methods for creating selvage edges,including looping the wires at the edge of the cloth.
Wire Used to Make Wire Mesh
The raw material of wire mesh is wire, they are more choose stainless steel wire woven, also useful black iron fund made or low carbon steel and high steel, used for the production of wire mesh has a variety of specifications, the conventional is circular wire, they use the diameter of the wire to express the thickness of the specification (translation of this paragraph instead of the following expression)
The different materials selected by the screen doomed his use scene or use part is different, such as:
Low carbon steel, its main component is iron, containing a small amount of carbon, is a low-cost, multi-purpose metal, mostly used for shields, isolation, and a certain surface treatment to achieve decorative effects.
Stainless steel, stainless steel according to the brand, has a strong and durable, with shiny luster, corrosion resistance, heat resistance and oxidation resistance, suitable for filtration, mining, chemical, construction and other industries, is a more commonly used material choice for woven wire mesh.
- Grade 304—has excellent corrosion,heat,and oxidation resistance and is one of the most widely used metal wires in the production of wire mesh.Much of its appeal is due to itsvery reasonable price.
- Grade 316—has excellent corrosion,oxidation,and heat resistance at temperatures of 1000 degrees Fahrenheit or higher.Additionally,it resists pitting in chloride environments due to its molybdenum content.
- Grade 310-It has excellent high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, its melting point is 1400 degrees, and it should be able to maintain good mechanical properties below 1150 degrees.
- Grade 321 —is austenitic 18/8 stainless steel that is stabilized with titanium.It is used for wire mesh for oil refineries.
- Grade 904—He called super stainless steel, has a strong corrosion resistance, has a high chromium content and enough nickel content, the addition of copper makes it have a strong acid resistance, especially to chloride gap corrosion and stress corrosion cracking has a high resistance, very unlikely to appear corrosion spots and cracks, the resistance to pitting slightly better than other steel
Aluminum Wire In Wire Mesh
Aluminum is lightweight,flexible,malleable,corrosion-resistant,and low priced.It is the most popular of the non-ferrous metals used to produce wire mesh.Aluminum grade 1000,pure aluminum,is seldom used to produce aluminum wire mesh.The majority of aluminum is alloyed with other metals such as copper,magnesium,zinc,or silicon in certainpercentages to increase the strength of aluminum as well as improve some of its other properties.
Alloys 1350,5056,and 6061 are the most commonly used for the production of aluminum wire mesh.
| Percentage of Aluminum Wire Mesh Alloys | ||||||||||
| alloy | si | fe | cu | mn | mg | cr | zn | ti | ga | aluminum |
| 1050 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 99.6 |
| 3003 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.05-0.2 | 1.0-1.5 | 0.8-1.3 | 0.1 | remainder | |||
| 5052 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.2-2.8 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.1 | remainder | ||
| 6005 | 0.6-0.9 | 0.35 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | remainder | ||
Copper In Wire Mesh
Copper wire mesh is ductile and malleable,with exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity.It is often usedfor radio frequency interference shields in Faraday cages and electrical applications.As with aluminum,copperis seldom used in its pure form and is usually alloyed to enhance and improve its natural properties.
Copper changes color when exposed to salt,moisture,and sunlight,from salmon-red to shades of brown togray and,finally,blue-green or gray-green.To avoid the change in the color of copper wire mesh,it is treatedwith coatings and chemicals,which speeds up or slows down the oxidation process.
Brass In Wire Mesh
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc.It is a soft,pliable metal known as 270 yellow brass or 260 high brass inwire mesh manufacturing.The chemical composition of 270 yellow brass is 65%copper and 35%zinc.With 260high brass,the chemical composition is 70%copper and 30%zinc.The increased content of zinc in brass wiremesh gives it high tensile strength and abrasion resistance and produces hardened mesh.
Industrial grade brass wire mesh has a yellow tint that makes it popular as a decorative artistic addition toarchitectural projects.
Bronze In Wire Mesh
Bronze is also an alloy of copper that consists of 90%copper and 10%zinc.It has the same properties ascopper,including malleability,ductility,and durability.Bronze has a higher resistance to corrosion than brassand is harder and less malleable than copper.It is used for industrial applications such as filtering andarchitectural applications.
The alloys and metals listed above are the more popular types of wire used to produce wire mesh.Othermetals that are used for custom wire mesh are titanium,Hastelloy,Monel 400,nichrome,Inconel,andtungsten.Essentially,any ferrous or non-ferrous metal that can be formed into a wire can be used to producewire mesh
Uses For Wire Mesh
There are endless uses for wire mesh patterns because they are adaptable and can meet any requirements.Industrial uses for wire mesh are as protective shielding,parts of filtration and separation systems,and railingsupports.Wire mesh is the primary part of filtration systems in wastewater treatment plants,petrochemicalfacilities,and juice production.
Aside from its industrial use,wire mesh has had commercial uses for many years as protection against insectsand as parts of animal enclosures.Screen doors,window screens,screen partitions,and decorative screensare produced using various forms of wire mesh.
Industries that rely on wire mesh are:
- Agriculture
- Automotive
- Building
- Chemical
- Coal
- Construction
- Food and Beverage
- Mining
- Petrochemical
- Plastics
- Pharmaceuticals
- Textiles
Commercial and residential uses for wire mesh include:
- Security Screens
- Fireplace Screens
- Stairwell Screens
- Gutter Guards
- Fencing
- Bird Screens
- Ventilations
- Window Screens
- Dog Cages
- Bird Feeders